How do hardlinks work together with rsync
People often ask how the rsync backup works and how hardlinks are used for this purpose.
The following article describes when files are created and deleted in the
file system and when hardlinks are created and
removed.
Hardlinks are a file system capability supported by the Linux file systems
ext3 and ext4. They are pointers that connect a file name with its
content on the file system. This means that hardlinks can be used to access files with
different names from different positions in the file tree.
The Linux command ln can be used for this purpose, for example.
During an initial rsync backup, all files are copied and saved in the
backup directory. For the second and each subsequent backup, only the files
that are new or have changed are copied again and deleted files are deleted.
As a result, all rsync backups except the first one are usually relatively fast, as long as the amount of data changed is kept within limits.
For all files that have not changed, hard links to the files are created in the backup directory to the files that were backed up in previous backups backups.
If files are deleted, the hard link to the previously backed up file, that exists in the previous backup is no longer created in the new backup and therefore the file in the new backup is removed.
This means that you always have full access to a backup status and unchanged files are not repeatedly backed up and take up disk space. This saves backup time and space.
A file is only deleted when it has no loner any hard links to it. This means that as long as there is still at least one backup that refers to the file via hard link, the file is not deleted and is available for a restore.
The following image shows graphically when hardlinks and files are created or deleted. There is also a corresponding Youtube video, including a demo on the system.
The following graphic shows when F2 in BD6 is deleted in the file system. However, this is only true if all backups containing F2 were deleted - i.e. BD1 - BD5.
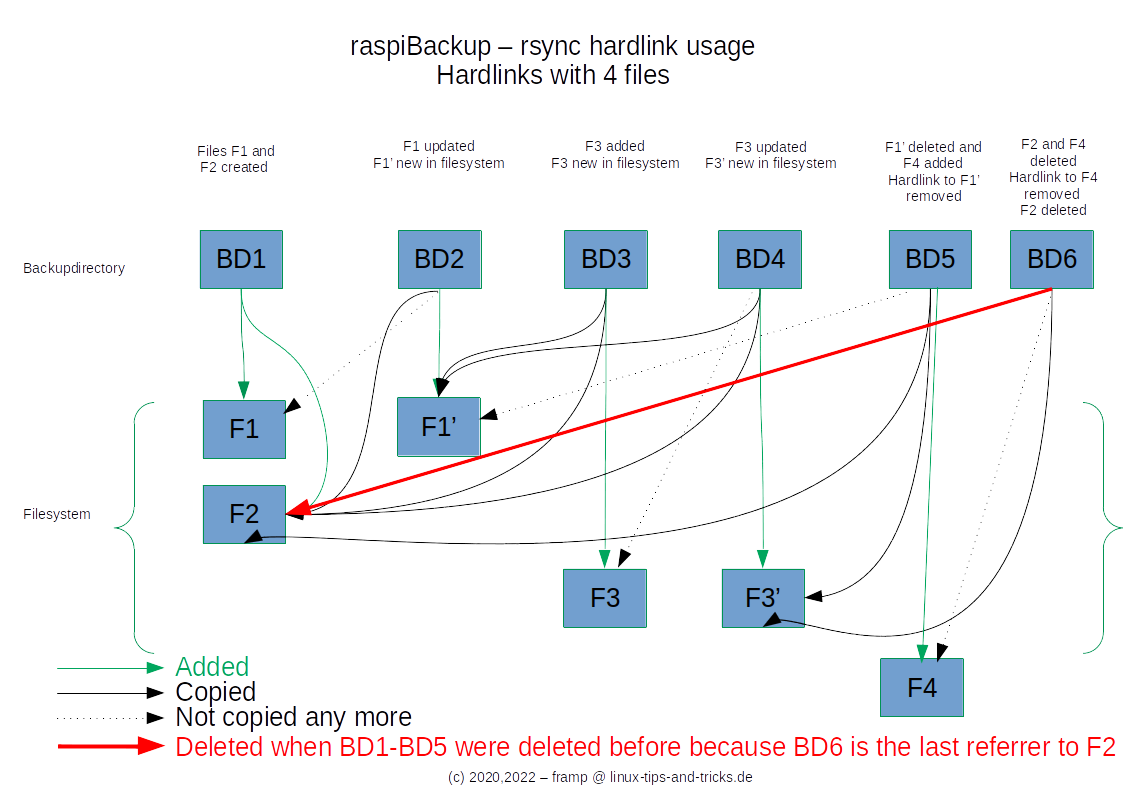
Many file managers show the disk space used without taking into account the space saved by hard links and are therefore much too high. This is especially true for Windows file managers.
The raspiBackup FAQ17 describes how to determine the disk space actually used when using hard links. disk space when using hardlinks can be determined.
Weblinks
- du counting harldinks towards filesize - An article that explains why the du command must be executed over multiple directories, to see the savings from hardlinks