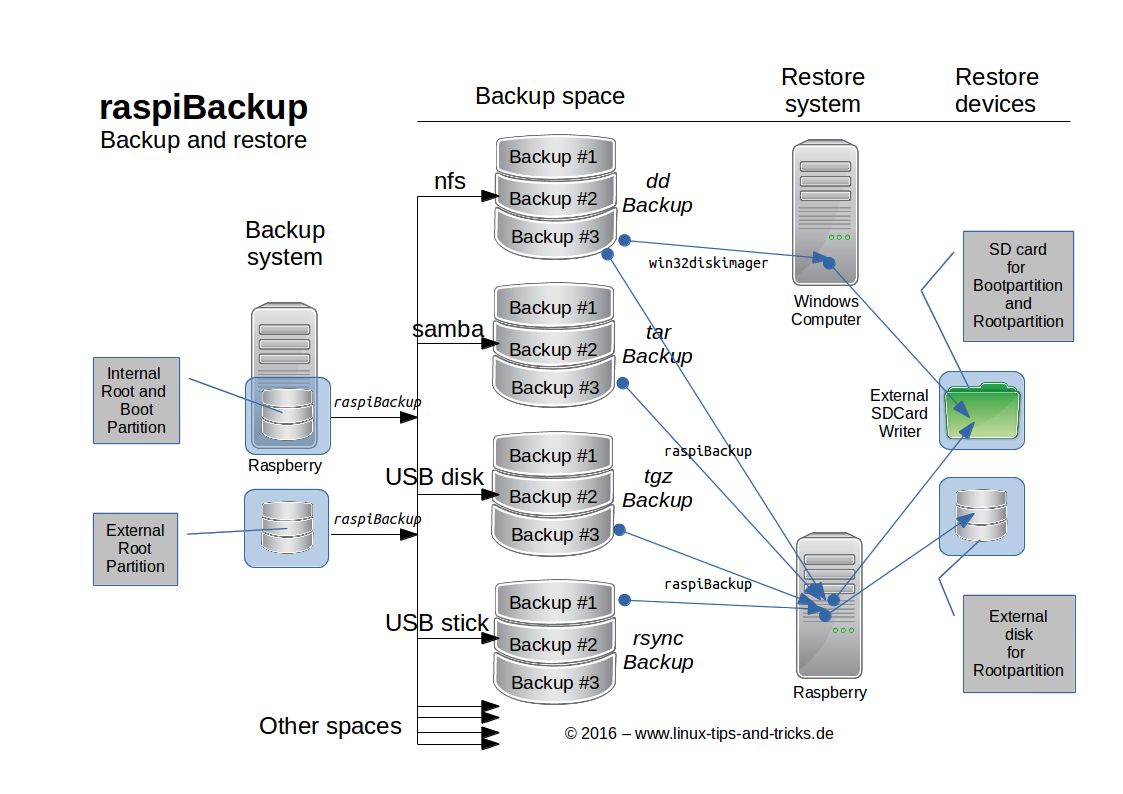
Function overview
With raspiBackup you can quickly and securely obtain a complete system backup of your Raspberries and a configurable backup history on a regular basis and can thus completely restore your Raspberry so that it boots again with an old backup status.
-
Automatic regular backup of a running Raspberry Pi (it backs itself up) See also Is a backup of a running system reliable? Shouldn't the entire system be stopped before the backup?
-
Full and incremental backups
- The backup type
rsynccreates complete and then incremental backups using hardlinks. - The backup types
ddandtaralways create complete backups (also zipped). Note: With theddbackup, you can activate the option that only the space occupied by the partitions and not the entire SD card is backed up.
- The backup type
-
Two backup strategies
- A defined number of backups are kept
- Backups are kept according to the grandfather-father-son backup strategy (GVS)
-
Two backup modes:
- the normal backup mode only backs up the boot and root partition
- the partition-oriented mode backs up any number of partitions on the system device.
Note: Only partitions on the system device are backed up. Backing up partitions of other devices is not supported. Larger amounts of data can be backed up by raspiBackup using partition-oriented backup if they are stored on other partitions of the system device, such as /dev/sda3 or /dev/mmcblk0p3
-
Any number of backups from the past can be stored
Not only a single backup is created, but also a backup history. You can either define a number of backups to be kept, or you use the GFS principle (in raspiBackup called "Intelligent Rotation Strategy" see Grandfather-father-son generation principle
-
An intelligent backup strategy is available For example, backups of the last 7 days, the last 4 weeks, the last 12 months and the last n years can be saved.
-
Simple installation with menu-driven installer (comparable to
raspi-config)The most important options of raspiBackup can be configured in German, English, Finnish, Chinese and French, so that the first backup in 5 minutes can be created.
-
Open source
raspiBackup is available under the GNU license as open source and free of charge. However, a donation is still welcome 😉
-
All other options, some of which are very powerful, are documented in detail and can be defined in a configuration file.
The individual backup types are described in detail here. There is also a decision tree, to quickly find the right backup type.
-
Any directories and files can be excluded from the backup
-
Different backup types can be mixed per system (e.g. one
rsyncbackup per day, oneddbackup per week) -
Automatic stopping and starting of active services before and after the backup
-
Backup of any number of Raspberries in a backup directory
-
Messages are supported in German and English, French or Finnish.
-
Notifications
The backup run messages can be sent from raspiBackup by e-mail or Telegram, Slack or PushOver. Smilies indicate the success or failure of the backup run. Other smilies inform about other important events such as the availability of a beta or a new release or a reminder to perform a restore test to test the backup integrity.
-
Supported email clients: mailx/mail, sendEmail, ssmtp and msmtp. Unsupported e-mail clients can be integrated using an e-mail plug-in.
-
Simple update of raspiBackup to the current version
-
Simple distribution of new script versions to a larger number of hosts
-
All boot modes are supported
- Boot from a USB device or SSD (USB boot mode): Both partitions are located on a USB device. Supported by the newer Raspberries since model 3B
- Boot from the SD card: Both partitions are on the SD card (every model)
- Mixed mode: Boot from the SD card and use the root partition from a USB device. This is necessary for older Raspberries that do not support USB boot
-
Any backup destinations are possible, e.g.
- External USB stick
- External USB disk or SSD
- SMB network drive
- NFS network drive
- SSHFS network drive
- WebDAV* network drive
- FtpFS network drive
- Generally any device that can be mounted under Linux
-
An external root file system on a hard disk or USB stick is automatically backed up in hybrid boot mode during normal backup mode and restored with
tarorrsync. -
Snapshots
So-called raspiBackup snapshots can be created manually.
These are named backups that are not deleted automatically. They are used, for example, to back up important intermediate steps during system upgrades to be able to revert to previous versions at any time in the event of problems. In contrast to normal backups a free selectable descriptive text will be be added to the backup directory. That way it's possible to identify the purpose of the snapshots.
-
Simple restoration of a backup
A backup of the
ddbackup type can also be restored from a Windows system. Win32Diskimager or similar tools can be used.tarandrsyncrequire a Linux system for a restore. It is recommended to use a preconfigured SD card with Raspberry Pi OS and start it on a Raspberry. -
Adaptation of
/etc/fstaband/boot/cmdline.txtto new UUIDs, PARTUUIDs or LABELs so that the system starts again immediately. -
Active social media channels
-
Notifications for new releases
As soon as a beta or a new release is available, raspiBackup writes a message indicating this. An upgrade is easy to perform. Likewise a downgrade back to a previous release.
-
Regression test suite
The basic functionality of raspiBackup (backup and restore) is automatically tested for all backup types and modes to ensure that the new raspiBackup release works as reliably as before.
-
Documentation
User manual with e.g. FAQs, configuration examples, NFS configuration, list of error messages and how to eliminate the error messages and much more is documented
-
Extension scripts
Various extension scripts are available.
They can extend the functionality of raspiBackup and can either be used unchanged or adapted to your own requirements.
For example, how pishrink can be used to make a
ddbackup even smaller or how a clone can be created in parallel in order to have an up-to-date boot medium that can be used at any time.An example script helps to perform further actions before and after the backup, such as mounting and unmounting the backup space.
And much, much more.
-
Extension points
For developers, raspiBackup offers various extension points, to perform pre- and post-processing during backup as well as during restore by your own code. For example there exists an extension which stops docker containers before the backup and starts them at the end again.
-
Backup of NVMe storage
Supported for Raspberry 5 and Compute Model 4 (CM4)
-
Supported operating systems
- RaspbianOS / Raspberry Pi OS
- Ubuntu
-
Simple system migration to other storage media
Each backup can be restored to an SD card, USB disk, SSD or NVMe SSD. And that easy the system has been moved to another device.
-
Support for Volumio
-
Support for gpt partitions